CDC(Change Data Capture),是数据库进行备份的一种方式,常用于大量数据的备份工作。本流程基于 MySQL binary log 来完成 MySQL CDC
适用场景
◇ MySQL 数据备份
◇ MySQL 数据迁移到其他类型数据库
◇ MySQL 数据同步另外一个数据库
实现方式
◇ 源 MySQL 库必须开启 binlog(8.0版本默认开启,8.0之前的版本默认不开启)
◇ 通过CaptureChangeMySQL组件监听指定库或者指定表
◇ 将获取到的binlog进行解析,转换成对应的SQL语句
◇ 对目标数据库执行上一步的SQL语句
优缺点
优点
- 非入侵式的备份方法,对源库影响较小
缺点
- 要求开启
binlog,MySQL 8.0 之前的版本默认不开启,开启binlog需要重启数据库服务
实现步骤
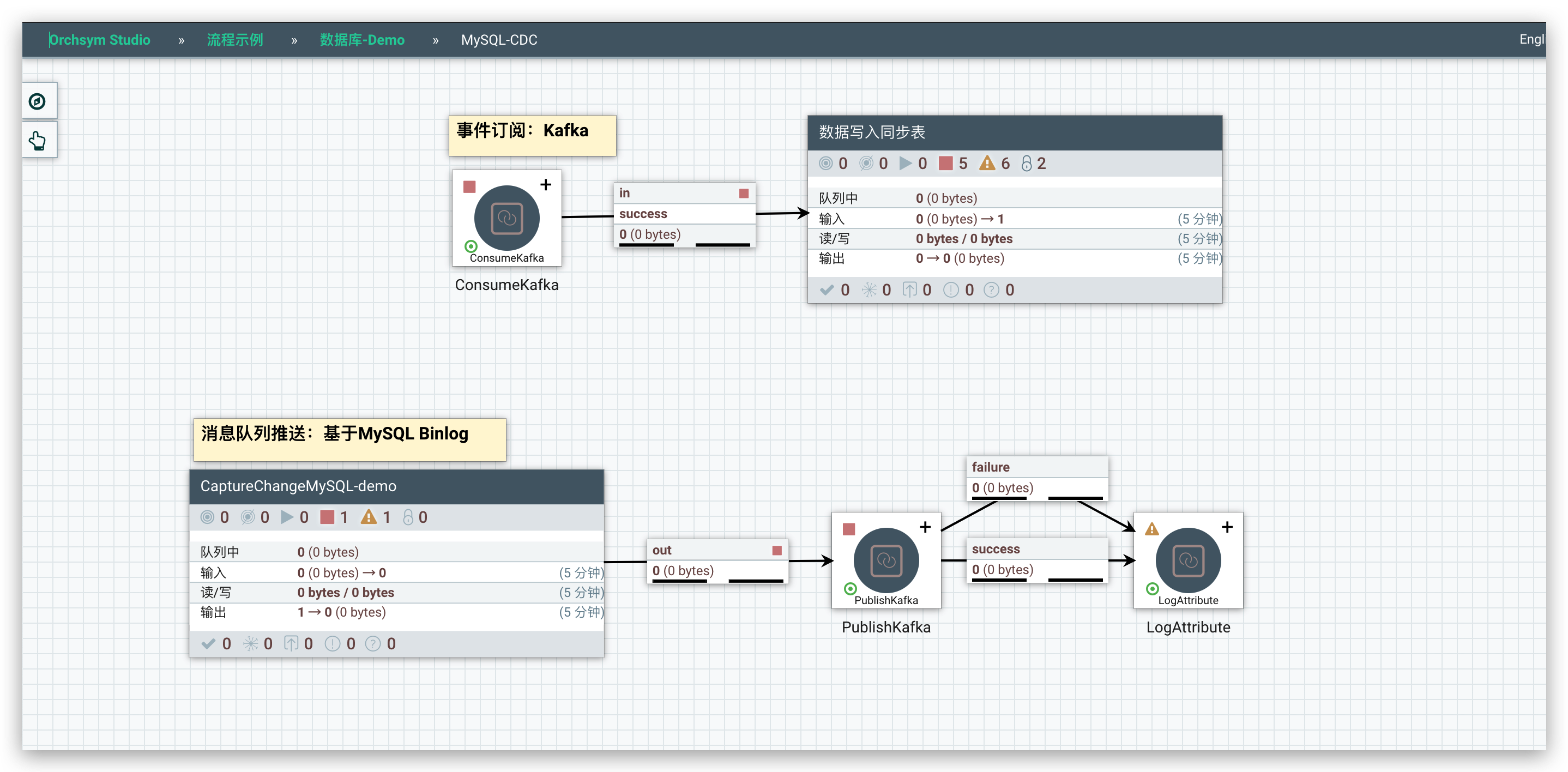
CaptureChangeMySQL配置监听的数据库/表信息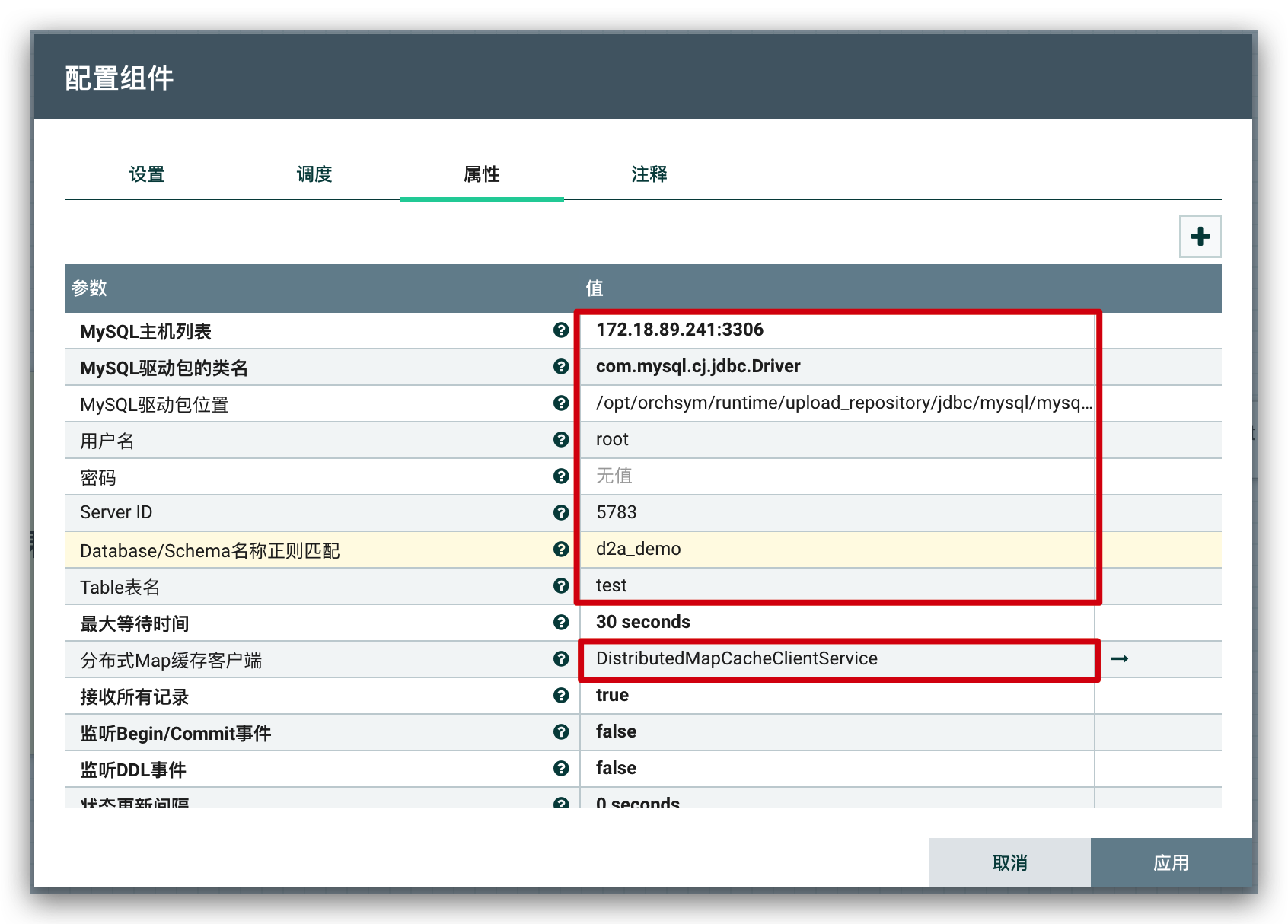
- 红框标注的是需要配置的部分
- Server ID 需要保证唯一
PublishKafka组件将binlog数据推送到 Kafka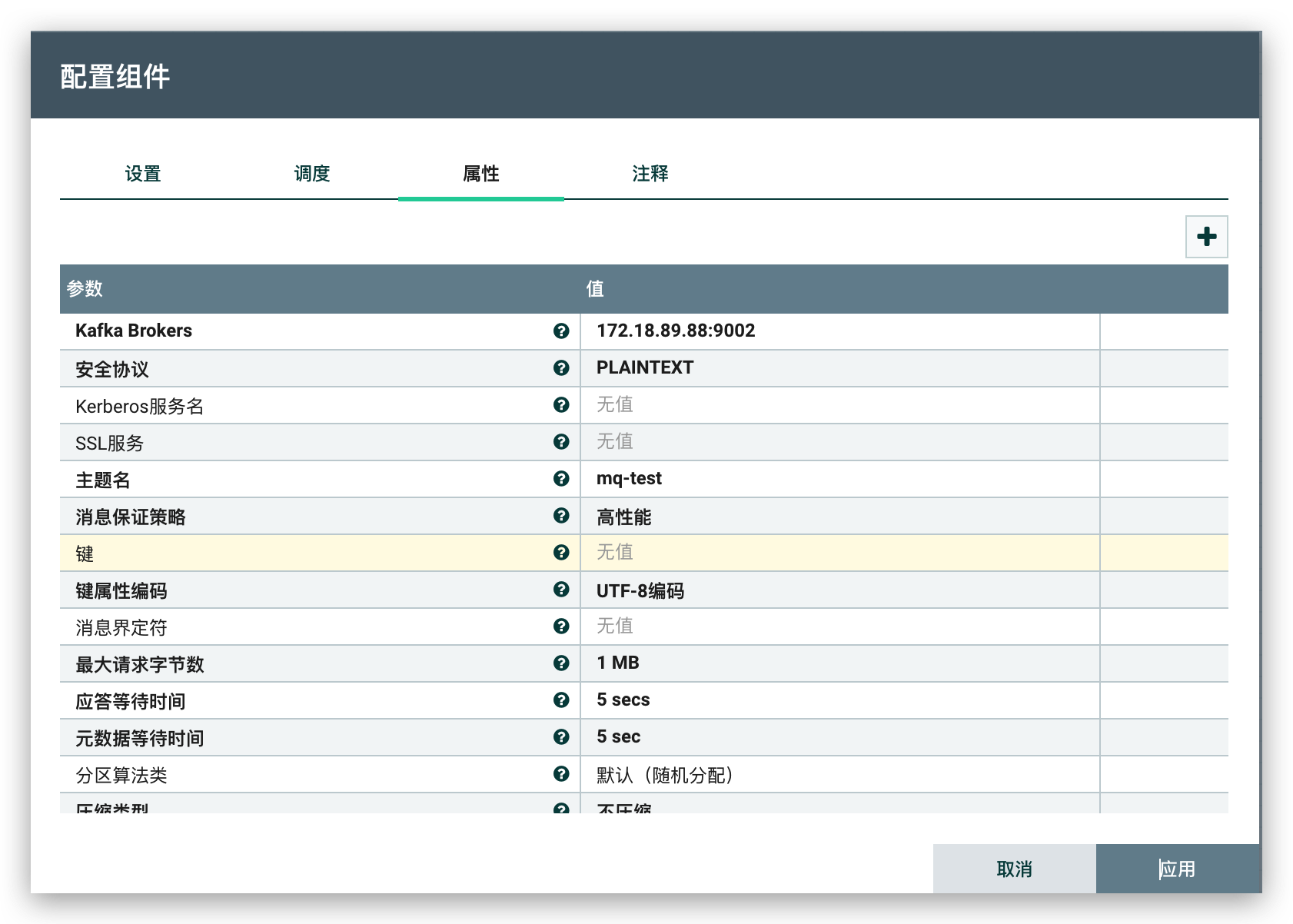
这里用消息队列来保证数据不丢失,同时,目标库可以通过消费消息来获取数据,方便同时对接多个目标库(也可以不用 Kafka)
消费端通过
ConsumeKafka消费 Kafka 消息,获取源库的binlog数据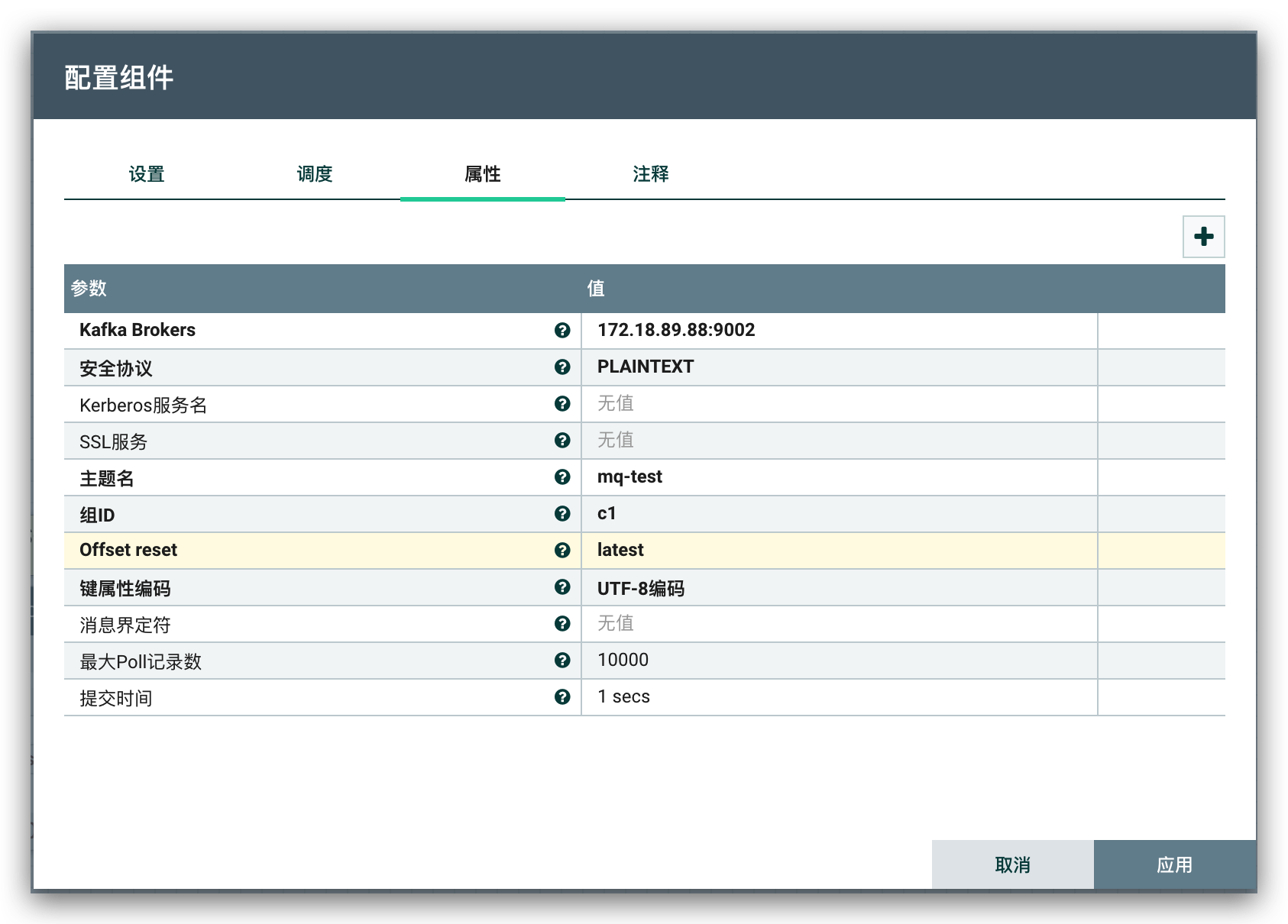
获取到
binlog数据(JSON格式),此时,通过EvaluateJsonPath组件来提取SQL的类型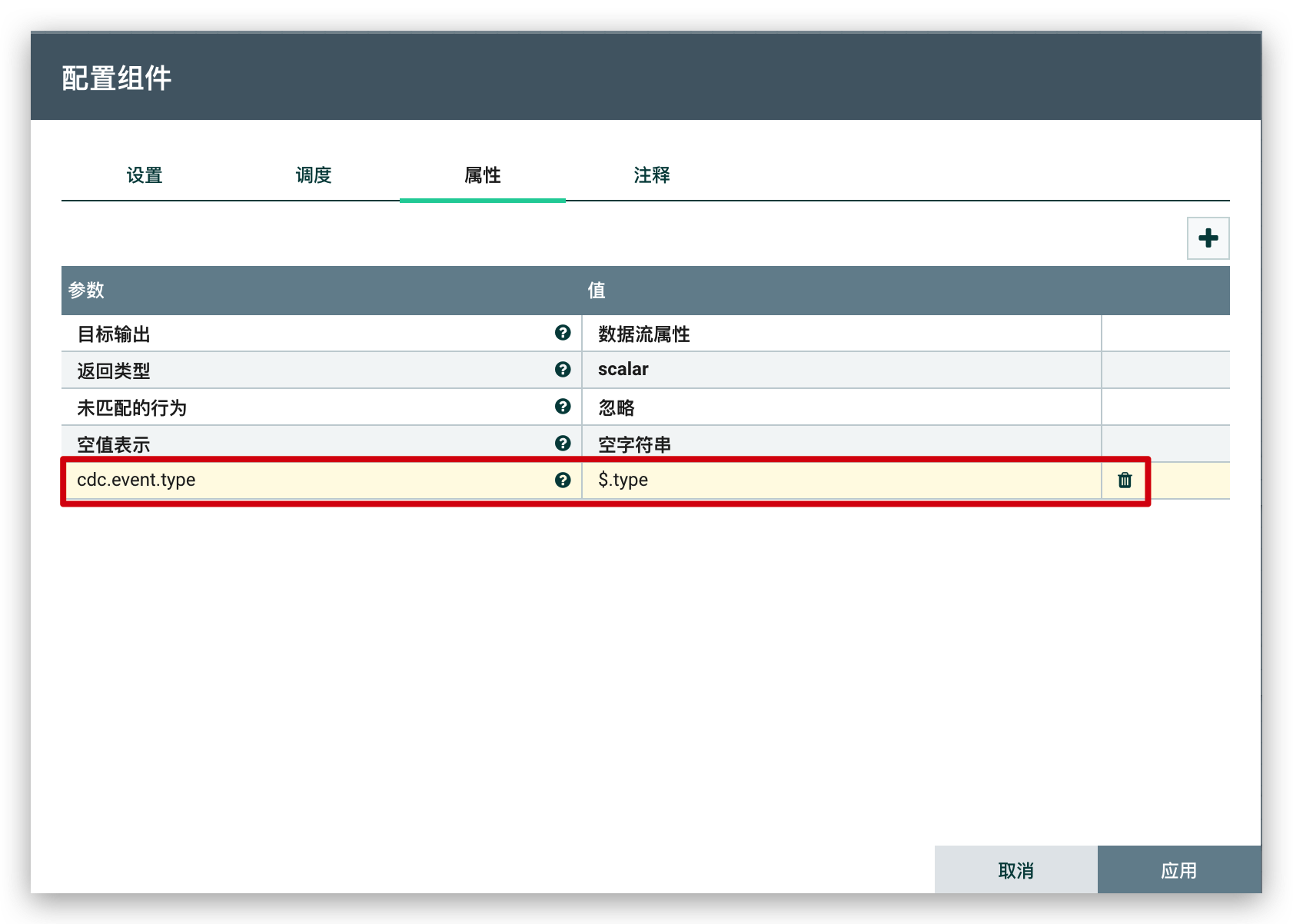
还需要对
binlog数据进一步处理,比如:获取表名、字段名、数据类型转换等等,这里通过脚本组件ExecuteScript来执行 Groovy 脚本处理数据转换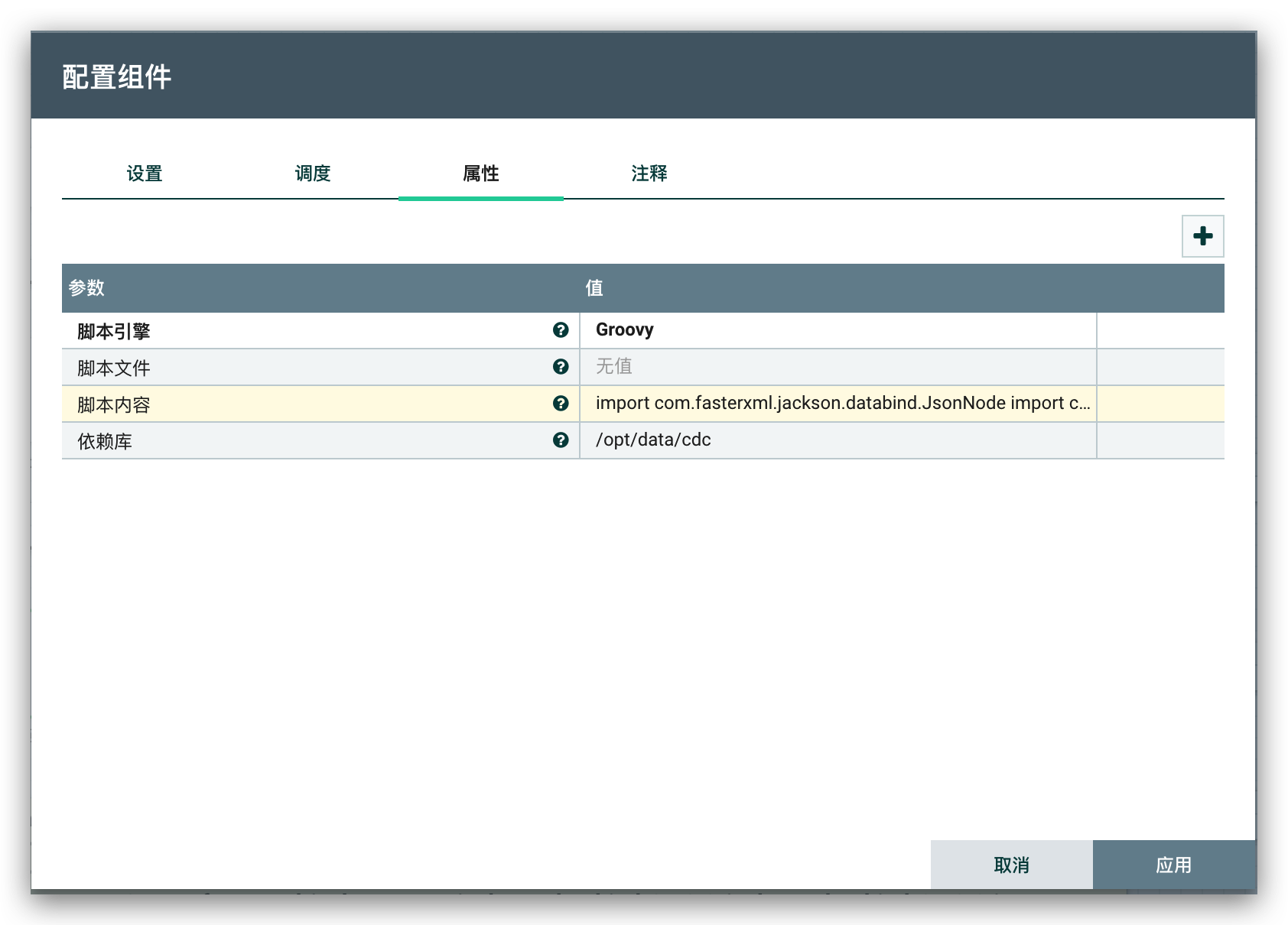
脚本内容:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils
import org.apache.nifi.flowfile.FlowFile
import org.apache.nifi.logging.ComponentLog
import org.apache.nifi.processor.ProcessContext
import org.apache.nifi.processor.ProcessSession
import org.apache.nifi.processor.Relationship
import org.apache.nifi.processor.io.InputStreamCallback
import org.apache.nifi.processor.io.OutputStreamCallback
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets
import java.sql.Time
import java.sql.Timestamp
ProcessSession current_session = session
ProcessContext current_context = context
ComponentLog current_log = log
Relationship SUCCESS = REL_SUCCESS
Relationship FAILURE = REL_FAILURE
FlowFile flowFile = current_session.get()
try {
String text = '{}'
current_session.read(flowFile, { inputStream -> text = IOUtils.toString(inputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) } as InputStreamCallback)
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper()
JsonNode data = mapper.readTree(text)
if (data.isEmpty()) {
current_session.transfer(flowFile, FAILURE)
}
JsonNode columns = data.path('columns')
Iterator<JsonNode> iterable = columns.iterator()
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>()
while (iterable.hasNext()) {
JsonNode column = iterable.next()
int type = column.get("column_type").asInt()
Object value = convert(column, type, "value",current_log)
if (value!=null){
map.put(column.get("name").asText(), value)
}
}
flowFile = current_session.write(flowFile, { outputStream ->
outputStream.write(mapper.writeValueAsString(map).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
} as OutputStreamCallback)
String tableName = data.get('table_name').asText()
current_session.putAttribute(flowFile, 'table_name', tableName)
current_session.transfer(flowFile, SUCCESS)
} catch (e) {
current_log.error(e.getMessage())
current_session.transfer(flowFile, FAILURE)
current_context.yield()
}
static Object convert(JsonNode column, int type, String label, ComponentLog log) {
Object value = null
JsonNode valueLabel = column.get(label)
if (valueLabel.isNull()) {
return value
}
try {
switch (type) {
case 12:
case 1:
value = valueLabel.asText()
break
case -4:
value = valueLabel.asText().getBytes()
break
case 4:
value = valueLabel.asLong()
break
case -6:
case 5:
value = valueLabel.asInt()
break
case -7:
value = valueLabel.asBoolean()
break
case -5:
value = new BigInteger(valueLabel.asText())
break
case 7:
value = new Float(valueLabel.asText())
break
case 8:
value = valueLabel.asDouble()
break
case 3:
value = new BigDecimal(valueLabel.asText())
break
case 91:
value = new java.util.Date(valueLabel.asText()).getTime()
break
case 92:
value = new Time(new java.util.Date(valueLabel.asText()).getTime())
break
case 93:
value = new Timestamp(new java.util.Date(valueLabel.asText()).getTime())
break
default:
value = valueLabel.asText()
break
}
} catch (e) {
log.error(e.getMessage())
}
return value
}脚本处理完
binlog返回数据后,就需要将数据写入目标表,此时,先通过UpdateAttribute组件设置目标表的表名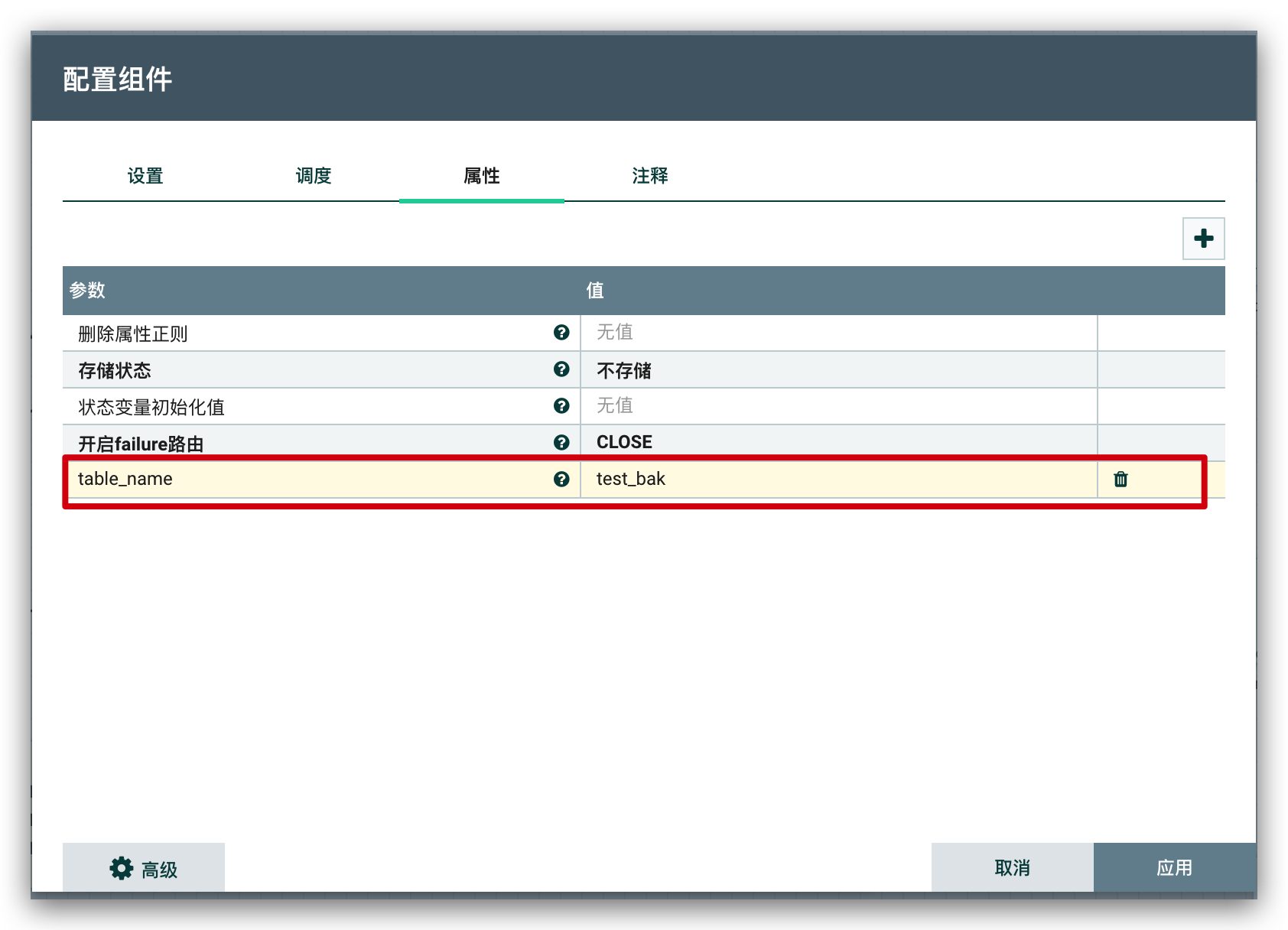
设置好目标表名后,需要根据前面所提取的
SQL类型来进行判断,决定执行的是什么类型的SQL语句,通过RouteOnAttribute组件来做判断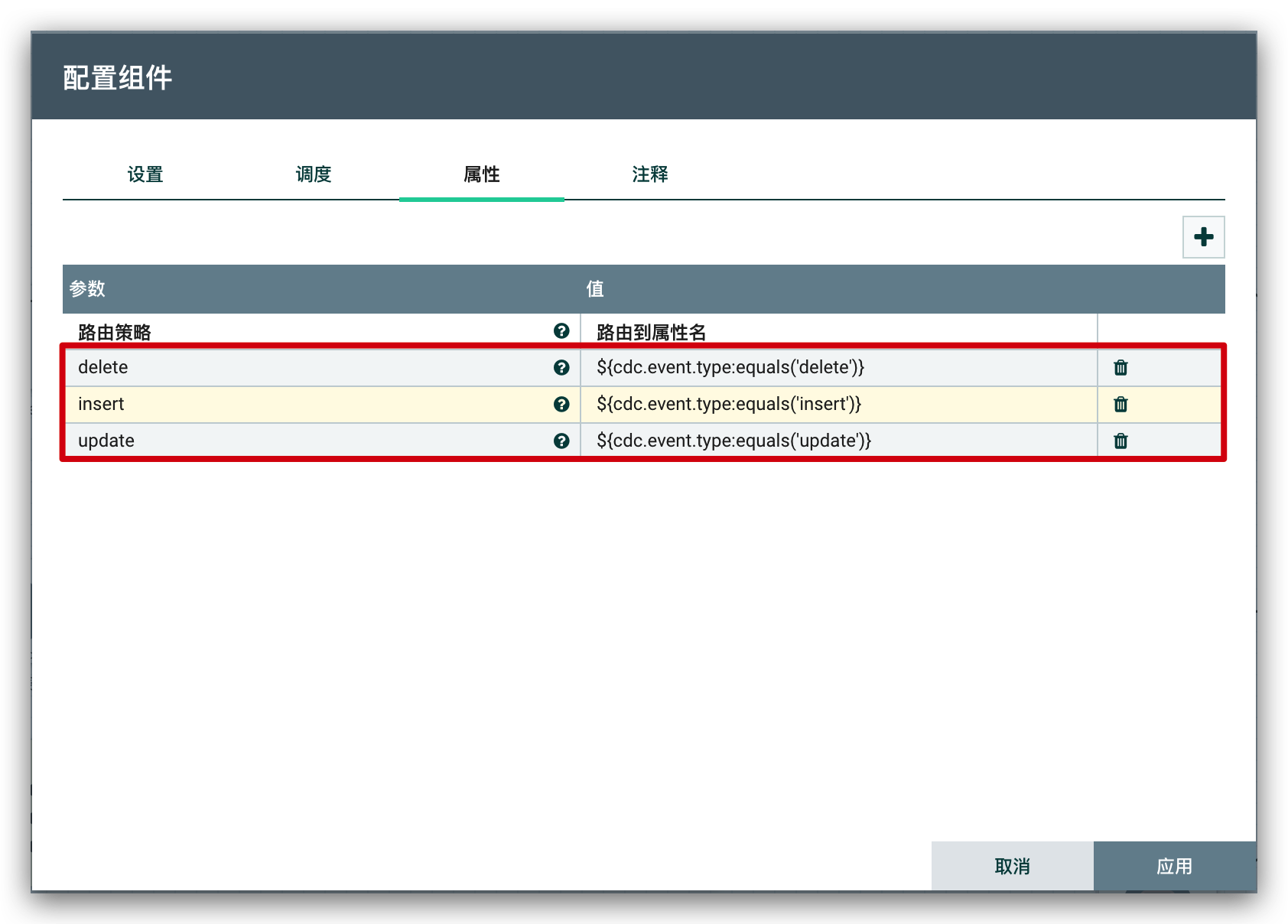
然后,通过
ConvertJSONToSQL组件,将binlog的 JSON 数据,转换成对应的SQL语句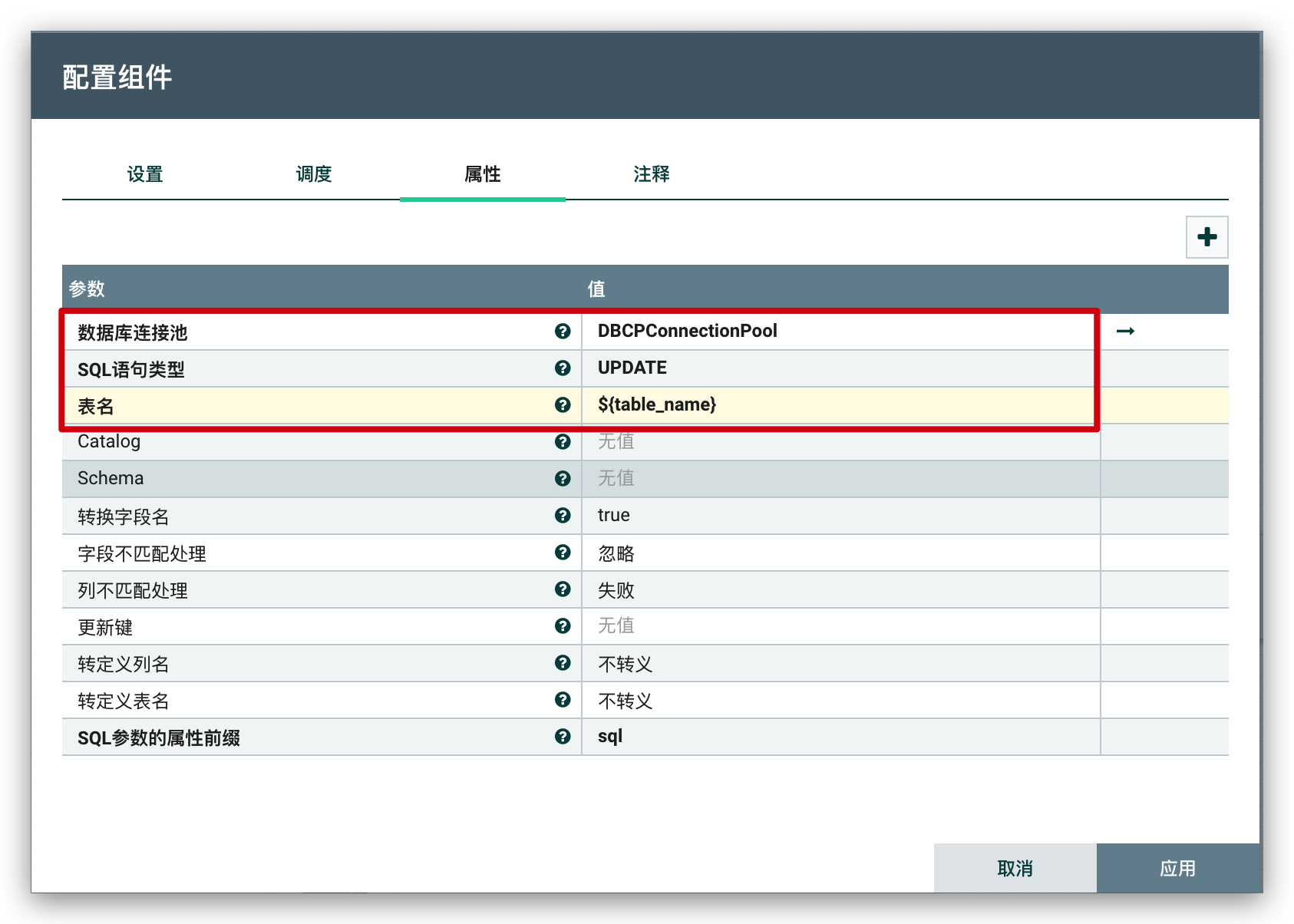
最后,通过
PutSQL组件执行SQL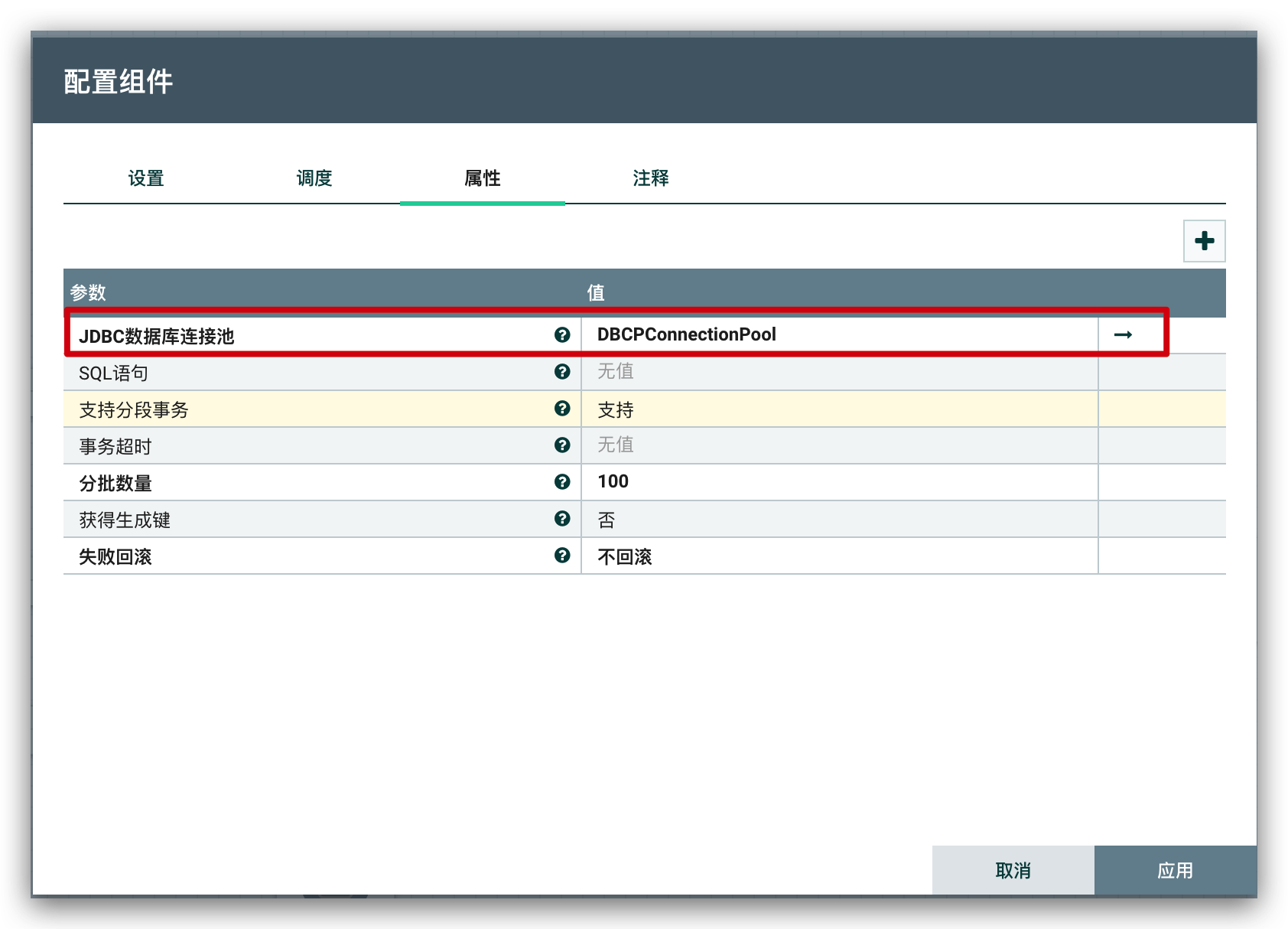
注意:
PutSQL的SQL语句属性要置空,SQL语句已经在前面通过ConvertJSONToSQL生成了,这里如果指定了,前面生成的SQL语句就不会执行了